Component Nodes
Components are available building blocks that define capabilities in SuperPlane. A component node is one instance of a component on the Canvas. When you add a component to your canvas, it becomes a node that can receive events, perform work, and emit payloads.
Components vs Component Nodes
Section titled “Components vs Component Nodes”- Component: The building block definition — what it does, what configuration it needs, what it emits
- Component Node: A single instance of a component placed on your canvas with specific configuration
Think of it like this: a component is like a blueprint, and a component node is the actual building you construct from that blueprint.
Component Types
Section titled “Component Types”There are two types of components:
Trigger Components
Section titled “Trigger Components”Trigger components start workflow executions. They listen for external events or can be invoked manually.
Examples: Webhook, Schedule, Manual Run, GitHub onPush, Slack onAppMention
Action Components
Section titled “Action Components”Action components execute operations in response to upstream events. They subscribe to events, perform operations, and emit payloads for downstream nodes.
Examples: HTTP Request, Filter, Approval, GitHub runWorkflow, Slack sendMessage
Adding Component Nodes to the Canvas
Section titled “Adding Component Nodes to the Canvas”New component nodes can be added to the Canvas in two ways:
From the Components Menu
Section titled “From the Components Menu”- Click the ”+ Components” button in the top right of the canvas
- Select a component from the list of available components
- Drag it onto the canvas where you want it
The component is now a node on your canvas, ready to be configured and connected.
From Output Channels
Section titled “From Output Channels”You can also drag an output channel from an existing node to an empty space on the canvas. This creates a new component node and automatically subscribes it to that output channel, making it faster to model workflows.
Node Overview on Canvas
Section titled “Node Overview on Canvas”Each component node on the canvas displays key information and provides interactive elements:

- Input channel — Drag to subscribe to events from other nodes (Action nodes only).
- Configuration overview — Quick summary of key settings for this node.
- Latest Run Item — Shows the last run executed or event emitted.
- Action menu — On hover: manually emit, copy, collapse/expand, or delete.
- Output channels — Subscribe other nodes or drag to create new components.
Component Node Sidebar
Section titled “Component Node Sidebar”Clicking on a component node selects it and opens a component node sidebar.
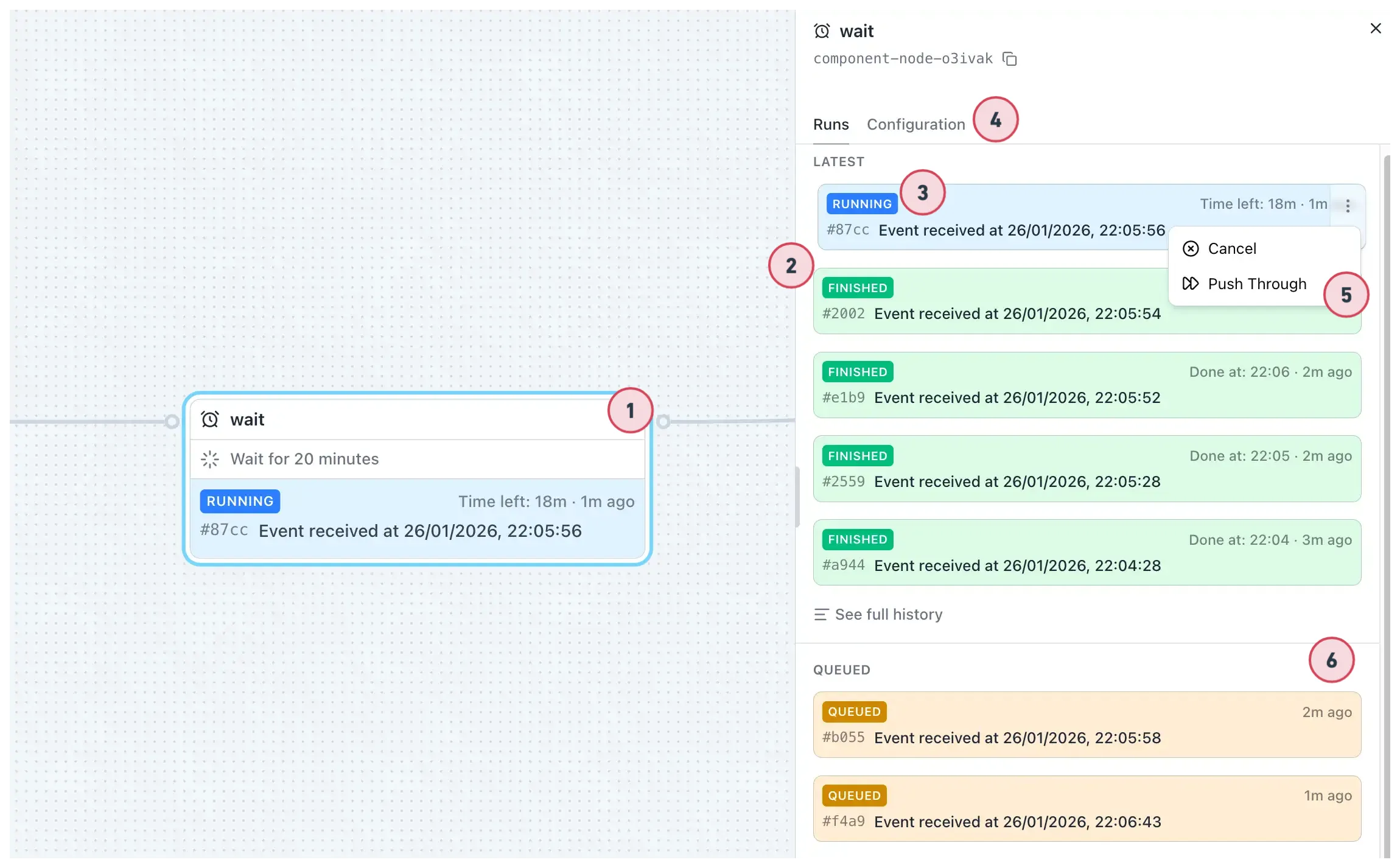
- Click to open — You can click on a node to open the sidebar.
- Resizable sidebar — Sidebar is resizable and contains node details.
- Latest runs section — Recent executions with event ID, timestamp, and status.
- Configuration tab — Settings for setting up and updating the node’s configuration. Each
component has its own configuration requirements (required fields, optional fields, and expression
support using
{{ }}syntax). - Action menu for run item — Cancel or push through running items.
- Queue — Items waiting to execute (FIFO order).
See Expressions for details on writing expressions.
Single Run Chain
Section titled “Single Run Chain”Select a run from the list to see the full chain of nodes it went through.
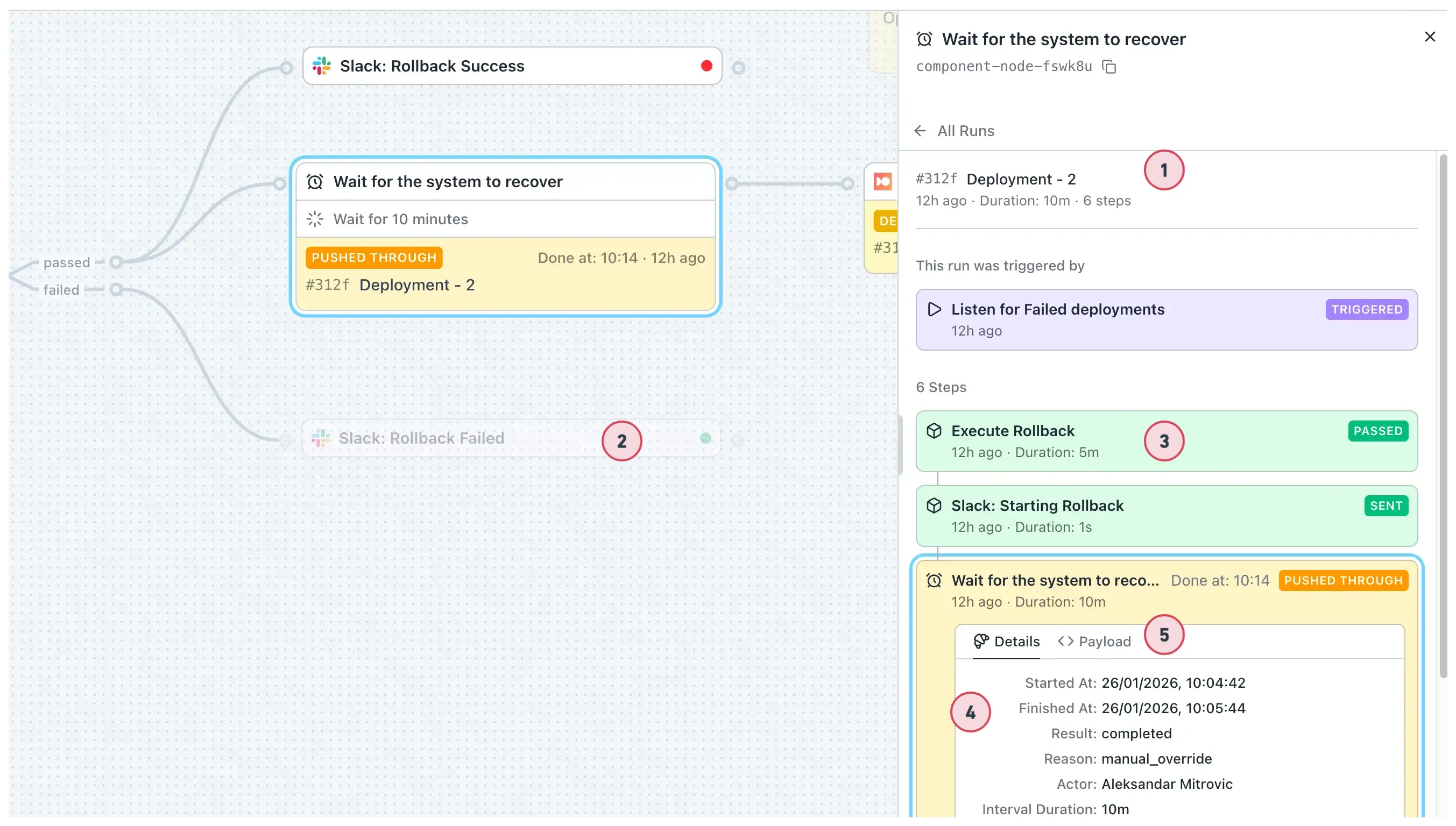
- Run chain — Shows all nodes in the run with current node preselected.
- Dimmed nodes — Nodes not included in the run are dimmed on the canvas.
- Expandable details — Expand other nodes in the chain to view their payloads.
- Details tab — Execution info: start/finish time, result, duration.
- Payload tab — The data this node emitted for downstream nodes.
Component Availability
Section titled “Component Availability”Components are provided by integrations. SuperPlane includes:
- Core components: Built-in components like Webhook, Filter, HTTP Request
- Integration components: Components from integrations like GitHub, Slack, PagerDuty
To use integration components, you may need to configure authentication or connection settings for that integration first.
Browse the Components section to see all available components and their documentation.
Best Practices
Section titled “Best Practices”When working with component nodes:
- Choose the right component: Understand what each component does before using it
- Use expressions: Make configurations dynamic by referencing upstream data
- Name nodes clearly: Use descriptive names that indicate purpose
- Test incrementally: Verify component behavior before building complex workflows
- Monitor run history: Check execution history to understand behavior and debug issues
For more details on how component nodes connect and how data flows between them, see Data Flow. For information about the canvas where you work with component nodes, see Canvas.